In alkyl halides the halogen atom is bonded to an alkyl group R. C H H H C H H Br alkyl halide C C H H H Cl vinyl halide I aryl halide.

Solved Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Begin Array L Text A Chlorobenzene Text B 1 Text Bromo 4 Chlorohexane Text C 1 2 Text Difluoro 3 Iodocyclohexane
Aryl halides are always ringed structures.

. Chloroethane was produced in the 15th century. They are further classified as primary secondary or tertiary according to the nature of carbon to which halogen is attached. An aryl halide is not just any halogen compound containing an aromatic ring.
The carbon atoms here are in a cyclic orientation. The halogen atom is bonded to the sp 2 - hybridised carbon atom of an aromatic ring. X is bonded to sp2 carbon on benzene ring.
Haloalkane or alkyl halides are the compounds which have the general formula RX where R is an alkyl or substituted alkyl group and X is a halogen F Cl Br I. Haloalkanes have been known for centuries. Define functional group and name the group present in each of the following structures.
Cl Cl 1-chloro-2-methylpropane 2R 3R 6S- 2 chloro 8 ethyl 36 dimethyl decane Cl Br Cl I F Br I Br F. Aryl halides are compounds containing halogen attached directly to an aromatic ring. If the compound is an alkyl halide indicate whether it is 1 2 or 3.
Download Alkyl Halide and Aryl Halide Chemistry notes for IIT-JEE Main and Advanced Examination. Draw structures for these alkyl and aryl halides Velvet manicure will make the nails manufactured like of velvet and they appear really soft for the contact. X is bonded to sp2 carbon of alkene.
FIGURE CANNOT COPY. The carbon-halogen bond is stronger than that of alkyl halides due to the presence of ring electrons. Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides.
Name and write the structures of. The general formula of aryl halides is ArX where Ar is phenyl substituted phenyl or aryl groups. Classify each halo compound shown below as an alkyl vinyl or aryl halide.
Which of these has weakest C CI bond. An aryl halide is a molecule having a halogen atom attached to an sp2 hybridized carbon in an aromatic ring directly. In this chapter we would focus on alkyl halides and aryl halides only under following subtopics.
Describe and compare the structures of alkyl halides and aryl halides. The below chart shows the boiling point of some simple haloalkanes. And also if it is allylic or benzylic.
Give IUPAC names for the following alkyl halides. A fluorine atom is. The same outcome is accomplished by a Specific powder flock thats sprinkled with nails.
Learnengineeringin collected the various Topic wise notes for JEEJoint Entrance ExamThis collection is very useful for JEE candidates to crack their upcoming JEE Examination. For example benzyl chloride is not an aryl halide because halogen is not directly. Name the type of organic compound each substance.
3 halides 2 halides 1 halides Alkyl halides also undergo ER in the presence of base as Nu Loss of HX and formation of bond H R OR CH2 CH2 Cl ROH CH3CHCH2 Cl CH3 ii In general 3 halides tend to react by elimination. Name the type of organic compound each substance. Draw the structures of all the alkyl halides that will be used in this experiment.
Alkyl halides have a linear or branched structure most of the times. Name these alkyl groups. Alkyl and Aryl Halides of Class 12.
They can also be manufactured from any organic precursors such as alkanes alkenes or alcohols and carboxylic acids. Consider all the primary halides in this experiment and rank them in order of reactivity in each reagent. An alkyl halide A on reaction with magnesium in dry ether followed by treatment with ethanol gave 2-.
The order of elimination reaction is. The halogen atom is bonded to an sp 2 -hybridised carbon atom of a carbon-carbon double bond. S N 1 S N 2 reactions.
Alkyl Halides RCX Alkyl halide X CC X Aryl halide Vinyl halide X F Cl Br I 101 Naming alkyl halides- Read 102 Structure of alkyl halides Table 101 Halomethane H3C-F H3C-Cl H3C-Br H3C-I Bond length pm 139 178 193 214 Bond strength KJmol 452 351 293 234 Dipole Moment 185 187 181 162 RCC _ Na CX H R H THF RCCC R H. Label each as primary secondary tertiary allylic or benzylic. PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF ALKYL HALIDES a Boiling point.
On the other hand aryl halides are organic compounds having halogen atoms bonded covalently to benzene rings or aromatic groups. Alkyl halide or haloalkanes are formed by the replacement of hydrogen atoms in an aliphatic hydrocarbon by halogen atoms Fluorine chlorine bromine or iodine. Aryl halides also show dipole-dipole interactions.
Circle any organic halide below that can undergo a S N1 or S N2 type substitution reaction. Draw structures for the following molecules. MAINIDEA Compare and contrast alkyl halides and aryl halides.
This is an unsaturated structure due to the presence of double bonds in the aromatic ring. They form a homologous series represented by C n H 2n1 X. Boiling points of haloalkanes Notice that three of these have bps below room temperature taken as.
Classes of Halides Alkyl. Draw structures for the following molecules. The systematic synthesis of such compounds developed in the 19th century in step with the.
The halogen atom is attached to a sp 2 hybridized carbon atom in aryl halides. Alkyl halides are organic compounds having halogen atoms covalently attached to aliphatic carbon atoms or carbon atoms in a straight hydrocarbon orientation. Many candidates are facing problems in collecting Maths Physics and Chemistry Topic wise.
Alkyl Halides and Aryl Halides 5 92 Structure of organic halides Because halogens are monovalent there arises little change in the structures of organic compounds when hydrogen atoms in them are substituted by halogen atoms. BPK 400 Room 300 temperature 200 100 0 CH 3 X CH 32 CH X CH 322 CH CH X Gas Gas Chlorides Bromides Iodides Figure 121. The carbon-halide bond of alkyl halides has a low density of electrons compared to aryl halides.
Generally alkyl halides contain hydrogen atoms attached to the sp. 1 halides by substitution and 2 halides by either or both of the reactions. Write the name and draw the structure of the alkyl group that corresponds to 0202.
If halogen is attached to a primary carbon atom in an alkyl halide the alkyl halide is called primary alkyl halide or 1 alkyl halide. Please draw the structures. Watch More Solved Questions in Chapter 22.
Halogen X is directly bonded to sp3 carbon. Define functional group and name the group present in each of the following structures. These alkyl halides are important because the halogens are a good leaving group that can easily react and allow the carbon to attach to something new.
MAINDEA Compare and contrast alkyl halides and aryl halides.
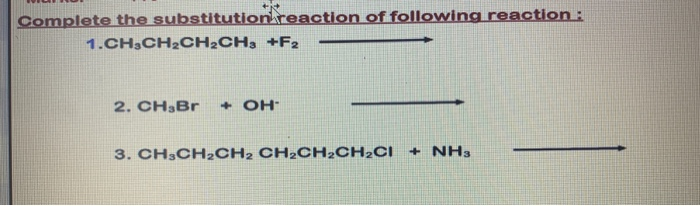
Solved 32 Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Chegg Com

Solved 32 Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Chegg Com
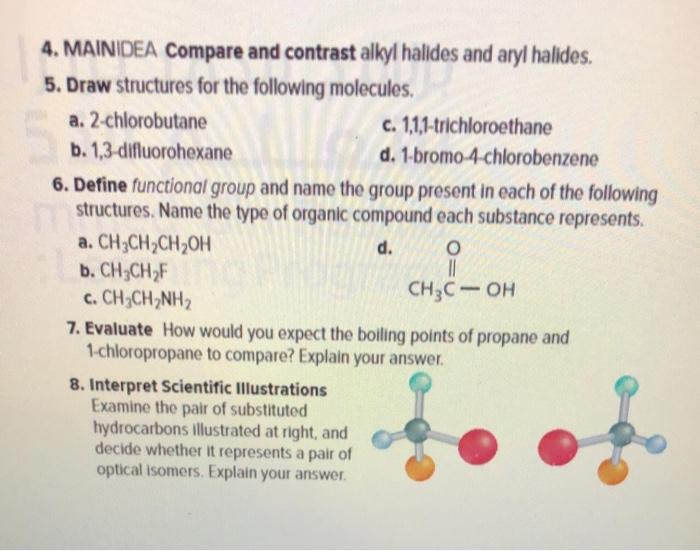
Solved 4 Maindea Compare And Contrast Alkyl Halides And Chegg Com
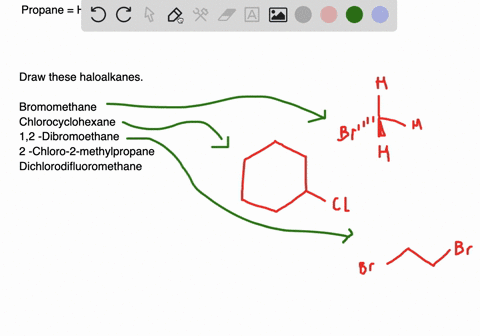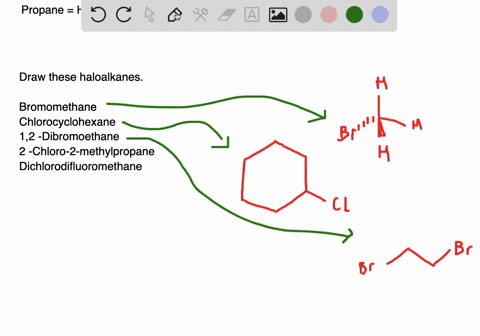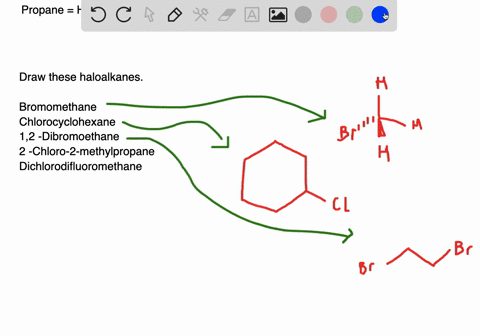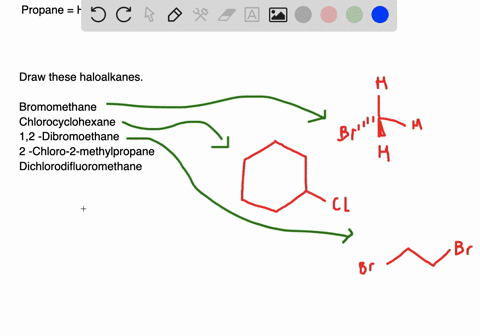
Solved Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Begin Array L Text A Chlorobenzene Text B 1 Text Bromo 4 Chlorohexane Text C 1 2 Text Difluoro 3 Iodocyclohexane

Solved Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Begin Equation Begin Array L Text A Chlorobenzene Text B 1 Text Bromo 4 Chlorohexane Text C 1 2 Text

Solved Xex Dx 32 Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Chegg Com
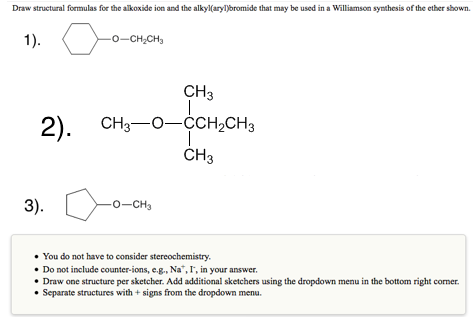
Solved Draw Structural Formulas For The Alkoxide Ion And The Chegg Com
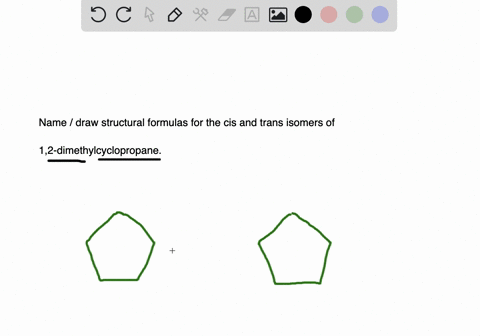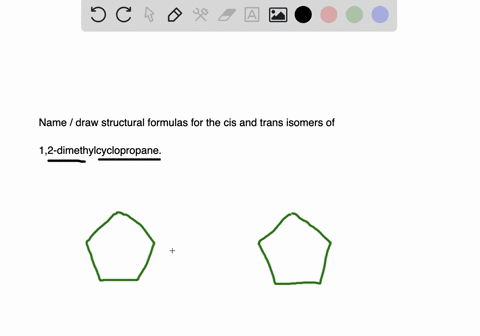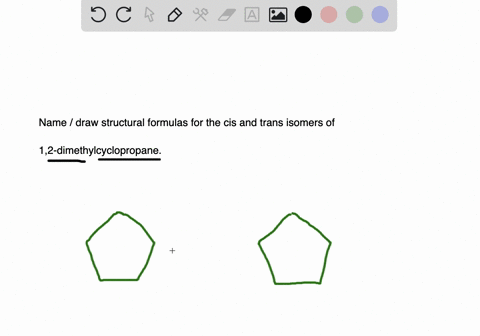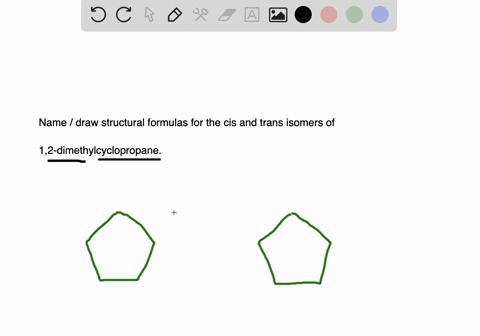
Solved Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Begin Array L Text A Chlorobenzene Text B 1 Text Bromo 4 Chlorohexane Text C 1 2 Text Difluoro 3 Iodocyclohexane
0 comments
Post a Comment